Sweet potatoes are a nutritious and versatile root vegetable that can be found in various colors, shapes, and sizes. They’re often praised for their health benefits, but not all sweet potatoes are created equal. In this article, we’ll dive deep into which sweet potato is the healthiest. We will explore their nutritional profiles, health benefits, and the best ways to prepare them. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which sweet potato to choose for your dietary needs.
Introduction
Which Sweet Potato is the Healthiest?
Sweet potatoes are a staple in many diets around the world. They come in various types, each with its unique flavor, texture, and nutritional profile. Knowing which sweet potato is the healthiest can help you make better dietary choices. In this section, we’ll provide an overview of the importance of sweet potatoes in your diet and introduce the different types available.
Importance of Sweet Potatoes in Diet
Sweet potatoes are rich in essential nutrients, making them a fantastic addition to your diet. They provide a good source of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. These nutrients play crucial roles in maintaining overall health, supporting immune function, and reducing inflammation. Including sweet potatoes in your meals can help you achieve a balanced diet and promote long-term wellness. Learn more about the importance of sweet potatoes in diet.
Different Types of Sweet Potatoes
When it comes to sweet potatoes, variety abounds. There are several types to choose from, each offering unique health benefits. Let’s take a brief look at some of the most common types you’ll encounter:
- Orange Sweet Potatoes: Known for their bright orange flesh and sweet flavor. They are rich in beta-carotene, which converts to vitamin A in the body.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes: These have vibrant purple flesh and are packed with anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants that offer numerous health benefits.
- White Sweet Potatoes: Less sweet and starchier than their orange counterparts. They offer a different nutritional profile that includes fewer antioxidants but more potassium.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Recognizable by their reddish skin and creamy white flesh. They have a distinct sweet flavor and are a favorite in Asian cuisines.
Explore more about purple sweet potato recipes.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the specifics of each type, comparing their nutritional content and health benefits to determine which sweet potato is the healthiest. This knowledge will empower you to make informed choices about incorporating these nutritious tubers into your diet.
Continue reading to discover the detailed analysis of each sweet potato type and how they compare nutritionally. This will set the foundation for understanding which sweet potato is the healthiest for your specific needs.
Types of Sweet Potatoes
Types of Sweet Potatoes
When considering which sweet potato is the healthiest, it’s crucial to understand the different types available. Each variety has distinct flavors along with textures and nutrition advantages.
Orange Sweet Potatoes
Orange sweet potatoes are the most common variety. They are known for their vibrant orange flesh and sweet, moist texture. But what makes them stand out nutritionally?
- Nutritional Profile:
- High in beta-carotene, which converts to vitamin A.
- Good source of fiber, aiding digestion and promoting gut health.
- Contains vitamins C and B6, as well as potassium and manganese.
- Health Benefits:
- Beta-carotene acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
- Vitamin A is vital to maintain eye health and immunity.
- Fiber material aids digestion and aids in regulating the blood sugar level.
Purple Sweet Potatoes
Purple sweet potatoes have a striking purple flesh and a mildly sweet flavor. They’re not only visually appealing but also pack a nutritional punch.
- Nutritional Profile:
- Rich in anthocyanins, potent antioxidants that give the potatoes their purple color.
- Contains significant amounts of vitamins A and C, as well as fiber.
- Health Benefits:
- Anthocyanins help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- High antioxidant content supports overall health and protects against oxidative stress.
- Fiber is beneficial for digestion and can benefit maintain the weight of a healthy person.
White Sweet Potatoes
White sweet potatoes differ from their colorful counterparts in flavor and nutritional content. They are starchier and less sweet, but still offer health benefits.
- Nutritional Profile:
- Lower in beta-carotene compared to orange sweet potatoes.
- High in potassium, which supports heart health.
- Contains vitamins C and B6.
- Health Benefits:
- Potassium regulates blood pressure and is beneficial to the cardiovascular health.
- Vitamin C helps boost the immune system and works in the role of an antioxidant.
- The fiber content aids digestion and promotes satiety.
Japanese Sweet Potatoes
Japanese sweet potatoes, with their reddish skin and creamy white flesh, are a favorite in many Asian cuisines. They have a unique, sweet flavor that distinguishes them from other types.
- Nutritional Profile:
- Rich in complex carbohydrates, providing a steady energy source.
- Contains vitamins A, C, and E, along with dietary fiber.
- High in antioxidants, similar to other sweet potato varieties.
- Health Benefits:
- Complex carbs offer sustained energy without causing blood sugar spikes.
- Vitamins and antioxidants support immune function and protect against disease.
- Fiber promotes digestive health and helps control appetite.
In comparing these types, it becomes clear that each has unique benefits. However, understanding the specific nutritional profiles and health benefits is key to determining which sweet potato is the healthiest for your dietary needs.
Next, we will delve deeper into the nutritional comparison of these sweet potato varieties. This will help us further analyze their benefits and ultimately decide which sweet potato is the healthiest.
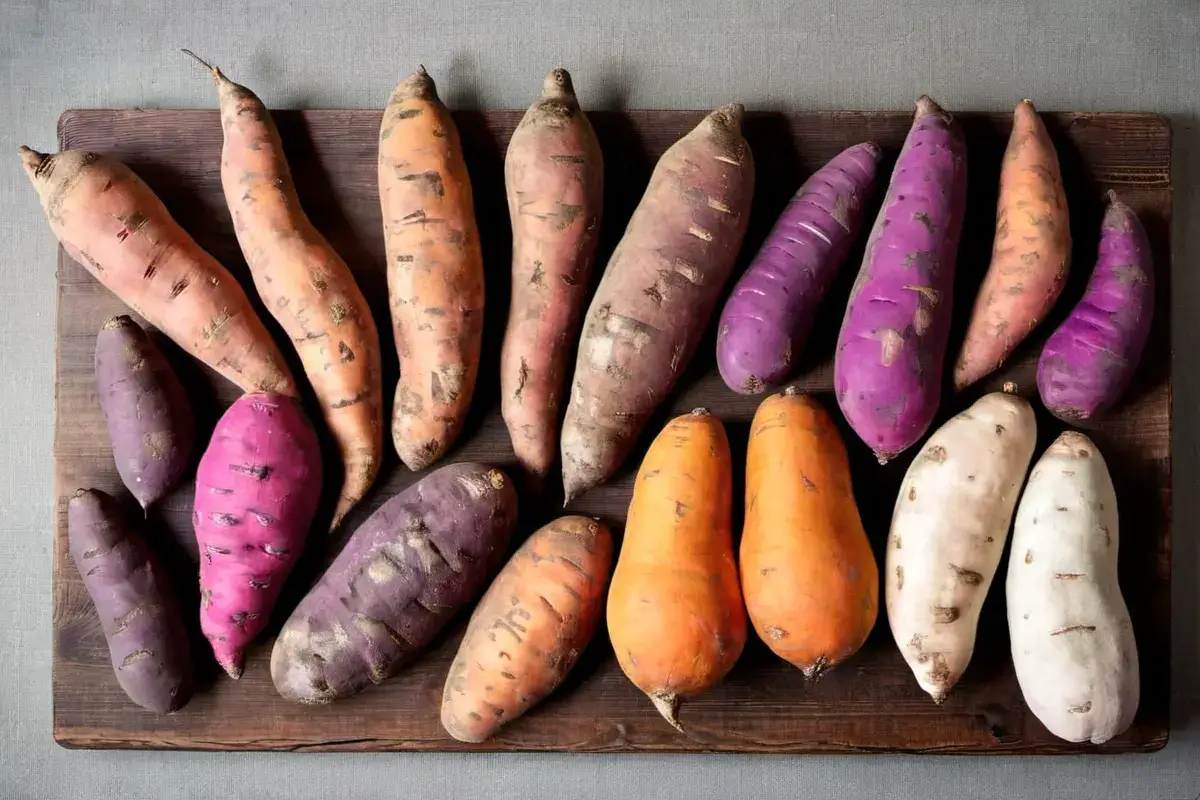

Nutritional Comparison of Different Sweet Potatoes
Nutritional Comparison of Different Sweet Potatoes
To decide which sweet potato is the healthiest, it’s essential to compare their nutritional profiles. Each variety has its strengths, and understanding these can help you make the best choice for your health goals.
Macronutrients
- Carbohydrates:
- Orange sweet potatoes are high in complex carbohydrates, providing a steady energy source.
- Purple sweet potatoes also offer substantial complex carbs but with the added benefit of antioxidants.
- White sweet potatoes contain more starch, making them higher in carbohydrates.
- Japanese sweet potatoes are similar to orange sweet potatoes in their carbohydrate content, offering a balanced energy source.
- Proteins:
- All sweet potatoes contain modest amounts of protein, with minor differences among the types.
- Fats:
- Sweet potatoes are naturally low in fat, making them a healthy choice for those monitoring their fat intake.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are crucial for maintaining health. Here’s a breakdown of each type:
- Vitamins:
- Orange Sweet Potatoes: High in beta-carotene (vitamin A), vitamins C, and B6.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes: Rich in vitamins A and C, with added anthocyanins.
- White Sweet Potatoes: Contains vitamins C and B6, though lower in beta-carotene.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Packed with vitamins A, C, and E.
- Minerals:
- Orange Sweet Potatoes: Good source of potassium and manganese.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes: Similar mineral content to orange varieties, with added antioxidants.
- White Sweet Potatoes: High in potassium.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Balanced mineral profile, supporting overall health.
Fiber Content
Fiber is vital for digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Here’s how each type compares:
- Orange Sweet Potatoes: High in dietary fiber, promoting gut health and satiety.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes: Rich in fiber and antioxidants, offering dual benefits.
- White Sweet Potatoes: Contains fiber, though slightly less than the orange variety.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Good fiber content, aiding digestion and weight management.
By comparing these nutritional aspects, we can see that each sweet potato type has unique strengths. For instance, if you’re looking for high beta-carotene, orange sweet potatoes are ideal. For antioxidants, purple sweet potatoes are the best choice. White sweet potatoes offer more potassium, while Japanese varieties provide a balanced mix of nutrients.
Next, we will explore the specific health benefits of these sweet potatoes in detail. This will further help determine which sweet potato is the healthiest based on individual health goals.
Health Benefits of Sweet Potatoes
Health Benefits of Sweet Potatoes
Understanding the health benefits of each type of sweet potato is crucial in determining which sweet potato is the healthiest. Each variety offers unique advantages, contributing to overall wellness.
Antioxidant Properties
- Orange Sweet Potatoes:
- A high concentration of beta-carotene, a substance your body converts into vitamin A. This vitamin is essential for vision, immune function, and skin health.
- Beta-carotene also acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting against oxidative stress.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes:
- Packed with anthocyanins, potent antioxidants that give these potatoes their vibrant color.
- Anthocyanins help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
- White Sweet Potatoes:
- Though lower in antioxidants compared to orange and purple varieties, they still provide a good amount of vitamin C.
- Vitamin C is essential for immune health and has antioxidant properties.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes:
- Contain a mix of beta-carotene and other antioxidants, offering a balanced benefit.
- These antioxidants benefit shield cells from damage, and also support overall health.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is linked to many health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. Sweet potatoes can help reduce inflammation thanks to their rich antioxidant content.
- Orange Sweet Potatoes:
- Beta-carotene helps combat inflammation, making these potatoes a good choice for reducing inflammation.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes:
- The high anthocyanin content makes these sweet potatoes particularly effective at fighting inflammation.
- White Sweet Potatoes:
- While not as rich in anti-inflammatory compounds, they still provide vitamin C, which helps reduce inflammation.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes:
- Offer a balanced anti-inflammatory effect due to their mix of antioxidants.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Managing blood sugar levels is essential, especially for individuals with diabetes or those looking to maintain stable energy levels. Sweet potatoes, with their low glycemic index, can help.
- Orange Sweet Potatoes:
- Have a lower glycemic index compared to regular potatoes, which means they cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
- The high fiber content also helps regulate blood sugar.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes:
- Similar to orange varieties, they have a low glycemic index and high fiber, aiding in blood sugar control.
- White Sweet Potatoes:
- Although higher in starch, they still have a lower glycemic index than regular white potatoes.
- The fiber content helps moderate blood sugar spikes.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes:
- Their balanced carbohydrate content and fiber help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Each type of sweet potato offers unique health benefits, from antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to aiding in blood sugar regulation. These benefits make sweet potatoes a valuable addition to any diet, contributing to overall health and well-being.
Next, we will explore the best sweet potatoes for specific health goals. This will provide a clearer picture of which sweet potato is the healthiest based on individual needs.
Link: Cooking Methods and Nutrient Retention
Best Sweet Potatoes for Specific Health Goals
Best Sweet Potatoes for Specific Health Goals
Identifying which sweet potato is the healthiest depends on your specific health goals. Different types of sweet potatoes offer varying benefits that can support specific health needs.
Weight Loss
For those looking to lose weight, sweet potatoes can be a valuable addition to a diet due to their high fiber content and low calorie count.
- Best Type: Orange Sweet Potatoes
- Reasons Why:
- The high fiber material will make you feel fuller longer, which reduces your overall caloric consumption.
- Lower glycemic index prevents spikes in blood sugar, promoting steady energy levels.
- Reasons Why:
Digestive Health
A well-functioning digestive system is vital to overall health. Sweet potatoes, with their high fiber content, can significantly contribute to gut health.
- Best Type: Purple Sweet Potatoes
- Reasons Why:
- Anthocyanins in purple sweet potatoes help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Reasons Why:
Athletic Performance
Athletes require foods that provide sustained energy and aid in recovery. Sweet potatoes are an excellent choice due to their complex carbohydrates and nutrient density.
- Best Type: Japanese Sweet Potatoes
- Reasons Why:
- High in complex carbohydrates, offering a steady release of energy.
- Rich in antioxidants and vitamins that help reduce oxidative stress and support recovery.
- Reasons Why:
Learn why sweet potatoes are great for athletic performance.
By understanding these specific health benefits, you can choose the type of sweet potato that aligns best with your health goals. Whether you’re aiming for weight loss, better digestive health, or improved athletic performance, there’s a sweet potato variety that fits your needs.
Next, we’ll discuss the best cooking and preparation methods for sweet potatoes. This will help you maximize their nutritional benefits and enjoy them in the healthiest way possible.
Cooking and Preparation Methods
Cooking and Preparation Methods
How you prepare sweet potatoes can significantly impact their nutritional value. To determine which sweet potato is the healthiest, it’s essential to consider the cooking methods that best retain their nutrients.
Boiling
Boiling is a common method for preparing sweet potatoes. It’s simple and preserves a lot of the nutrients, especially when the cooking water is used in soups or stews.
- Impact on Nutrient Retention:
- Boiling can help retain more beta-carotene than other cooking methods.
- However, some water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C can leach into the cooking water.
Baking
Baking is another popular method that enhances the natural sweetness of the potatoes. It’s a convenient way to prepare them without losing too many nutrients.
- Impact on Nutrient Retention:
- Baking retains most of the vitamins and minerals, including beta-carotene and fiber.
- It also caramelizes the natural sugars, making the potatoes taste sweeter.
Steaming
Steaming is an excellent method for preserving nutrients. It uses less water than boiling and doesn’t involve direct exposure to high heat.
- Impact on Nutrient Retention:
- Steaming preserves the highest amount of vitamins compared to boiling and baking.
- It also maintains the potato’s natural flavor and texture.
Frying
Frying sweet potatoes can enhance their flavor but can also add unhealthy fats and calories.
- Impact on Nutrient Retention:
- Frying can lead to significant nutrient loss and adds unhealthy fats.
- While it may improve taste, it is not the healthiest method.
Raw Consumption
Eating sweet potatoes raw is less common but can be done, especially in salads or smoothies.
- Impact on Nutrient Retention:
- Raw sweet potatoes retain all their nutrients.
- However, they can be harder to digest and may contain anti-nutrients that interfere with nutrient absorption.
Best Cooking Method for Maximum Health Benefits
Considering nutrient retention and health benefits, steaming and baking are the best methods for cooking sweet potatoes. These methods preserve the most nutrients while enhancing the natural flavors.
Each cooking method has its pros and cons, but choosing the right one can help you get the most out of your sweet potatoes. By understanding how different methods affect the nutritional content, you can better determine which sweet potato is the healthiest and how to prepare them for maximum benefit.
Conclusion
After thoroughly examining the different types of sweet potatoes, their nutritional profiles, and the best preparation methods, it’s time to conclude which sweet potato is the healthiest. Each variety has its unique strengths, making them beneficial for different health goals.
- Orange Sweet Potatoes: High in beta-carotene, excellent for vision and immune health, making them ideal for those needing a vitamin A boost.
- Purple Sweet Potatoes: Packed with anthocyanins, these are fantastic for reducing inflammation and providing powerful antioxidants.
- White Sweet Potatoes: Higher in potassium, they support heart health and blood pressure regulation.
- Japanese Sweet Potatoes: Offer a balanced mix of nutrients, making them perfect for sustained energy and recovery, particularly beneficial for athletes.
While all these varieties are healthy choices, the title of the healthiest sweet potato can depend on individual health needs. However, if one must be chosen, orange sweet potatoes stand out due to their exceptionally high beta-carotene content, which provides significant antioxidant benefits and supports immune health.
Incorporating a variety of sweet potatoes into your diet can help you reap the diverse benefits they offer. Try different kinds of food and preparation techniques to discover the one that is the perfect for you.
FAQs
To further help you understand which sweet potato is the healthiest, here are some frequently asked questions and their answers:
Q: Are sweet potatoes healthier than regular potatoes? A: Yes, sweet potatoes generally have more vitamins and fiber compared to regular potatoes. They also have a lower glycemic index, which means they cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels.
Q: Can sweet potatoes help with weight loss? A: Yes, sweet potatoes are high in fiber, which can help you feel full longer and reduce overall calorie intake. Their low glycemic index also helps maintain stable energy levels.
Q: How do sweet potatoes benefit skin health? A: Sweet potatoes are rich in beta-carotene, which converts to vitamin A in the body. Vitamin A is essential for skin health, helping to maintain healthy skin and reduce signs of aging.
Q: Is it better to eat sweet potatoes raw or cooked? A: Cooking sweet potatoes is generally better as it makes them easier to digest and enhances their natural sweetness. However, raw sweet potatoes retain all their nutrients and can be consumed in salads or smoothies.
Q: What is the best way to store sweet potatoes? A: Store sweet potatoes in a cool, dark place with good ventilation. Avoid refrigerating them as cold temperatures can affect their texture and flavor.
By addressing these common questions, we hope to provide a comprehensive understanding of the health benefits and versatility of sweet potatoes. This knowledge will help you make informed choices about which type of sweet potato to include in your diet, based on your specific health goals.